
lab practical 1 Anatomy & Physiology 2451 with Dr. Pesthy at Texas
Nasal Group. The nasal group of facial muscles are associated with movements of the nose and the skin surrounding it.. Nasalis. The nasalis is the largest of the nasal muscles and is comprised of two parts: transverse and alar.. Attachments: Transverse part - originates from the maxilla, immediately lateral to the nose. It attaches onto an aponeurosis across the dorsum of the nose.
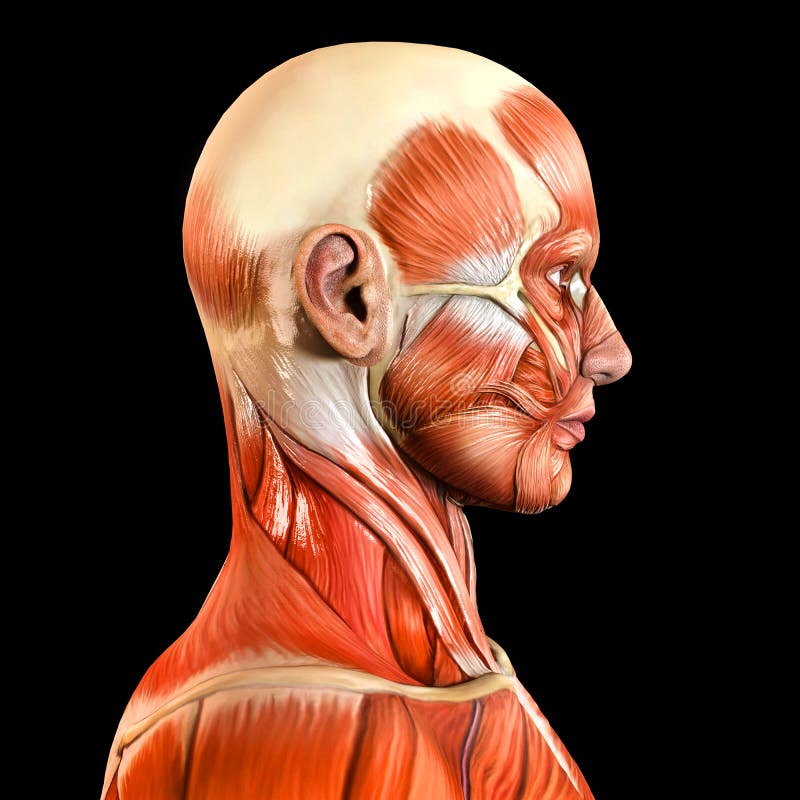
Lateral Side Facial Face Muscles Stock Photo Image 48360396
Age: 40 years Gender: Female x-ray Caldwell (OF15-20°) Waters (OM0°) Lateral Normal examination. No displaced facial or skull fracture noted. Case Discussion This case is an example of a normal facial bones series comprising of the Caldwell (OF15-20°), Waters (OM0°) and lateral views. 4 articles feature images from this case

Face anatomy, Anatomy, Human anatomy
Superior Thyroid Artery. Temporalis Muscle. Lateral view of left face and neck areas. For orientation, superior is toward the top of the image, anterior is toward the left border. The masseter muscle attaches to the zygoma and zygomatic arch and to the ramus and angle of the mandible. The temporalis muscle is seen superior to the zygomatic arch.

Anatomy and Physiology Axial Muscles of the Head, Neck, and Back
The curved part of a bone that gives structural support to the rest of the bone. Above: Markings of the facial bones with the following views: (A) anterior view, (B) lateral view of the left side of the skull, (C) inferior view with the mandible removed, and (D) lateral view of the right side of the skull. Marking.

Muscle of the head, lateral view, illustration Stock Image C039
It refers to the area that extends from the superior margin of the forehead to the chin, and from one ear to another. The basic shape of the human face is determined by the underlying facial skeleton (i.e. viscerocranium ), the facial muscles and the amount of subcutaneous tissue present.

Anterior and lateral view of the face showing the landmarks. Download
The lateral paranasal sinuses and facial bones view is a nonangled lateral radiograph showcasing the facial bones (i.e. mandible, maxilla, zygoma, nasal, and lacrimal bone) and paranasal sinuses. Indications This view is useful in assessing any inflammatory processes or fractures to the facial bones, orbits, and paranasal sinuses.

Pin on Muscles of the Face
Objective: To characterize the fixation patterns and gaze patterns of the face in lateral view. Design, Setting, and Participants: This was a prospective randomized controlled trial at an academic tertiary medical center.

6 Lateral view of the Facial Muscles Download Scientific Diagram
The skull is the skeletal structure of the head that supports the face and protects the brain. It is subdivided into the facial bones and the cranium, or cranial vault ( Figure 7.3.1 ). The facial bones underlie the facial structures, form the nasal cavity, enclose the eyeballs, and support the teeth of the upper and lower jaws.

SKULL LATERAL VIEW
Mandible Oblique Lateral Recumbent Mandible Inferosuperior Projection Intraoral Mandible Verticosubmental Projection The skull consists of 8 cranial bones and 14 facial bones. We have a separate article on radiographic positioning of the skull.
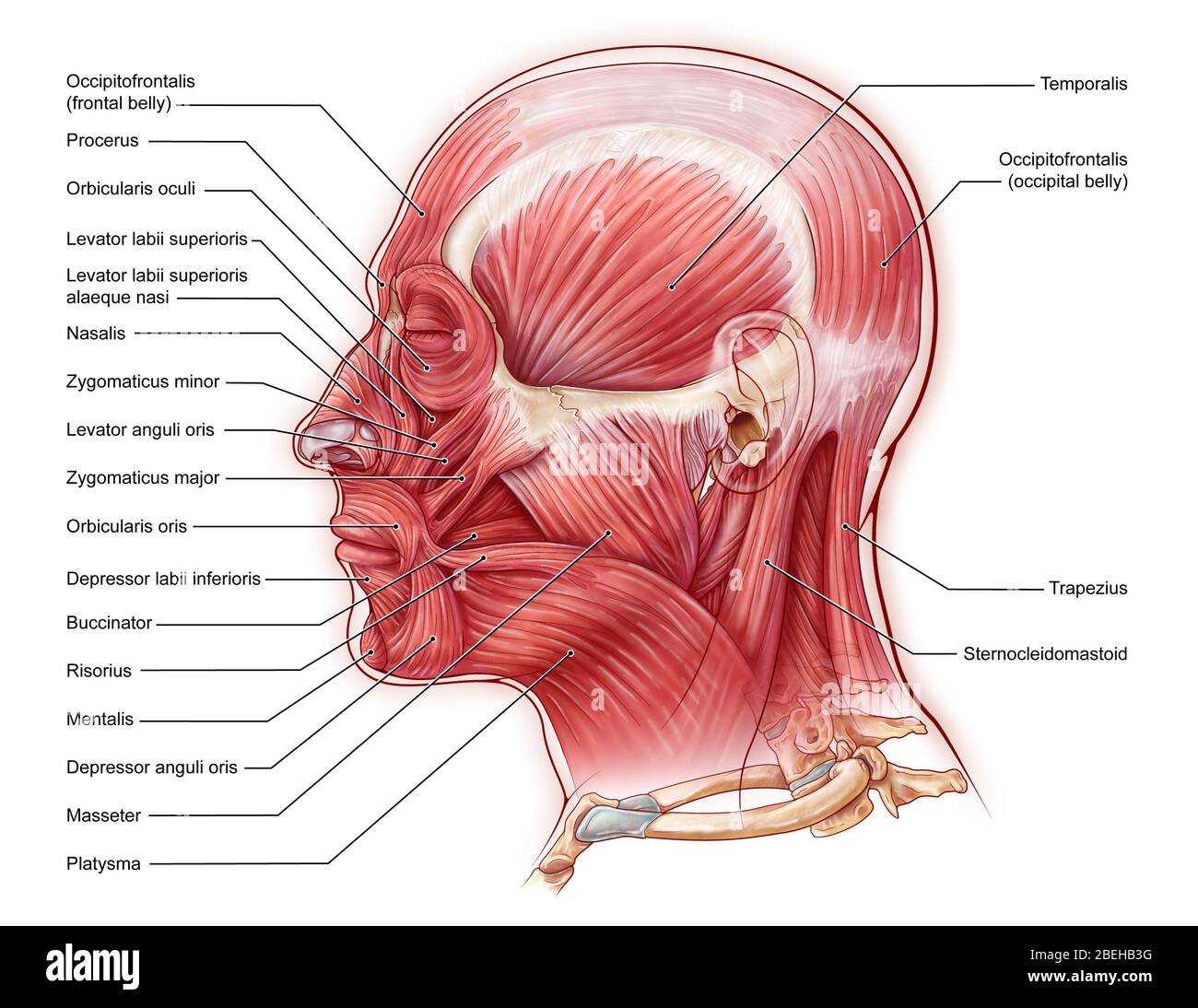
Zygomaticus major hires stock photography and images Alamy
A lateral view of the cranium and face shows bony landmarks. Figure 3. Open in figure viewer PowerPoint. Anthropological landmarks of the face, frontal view, which are described in this paper.. Apparently excessive posterior sloping of the forehead in a lateral view. subjective. Comments: Measurement requires an angle meter, inclined on the.
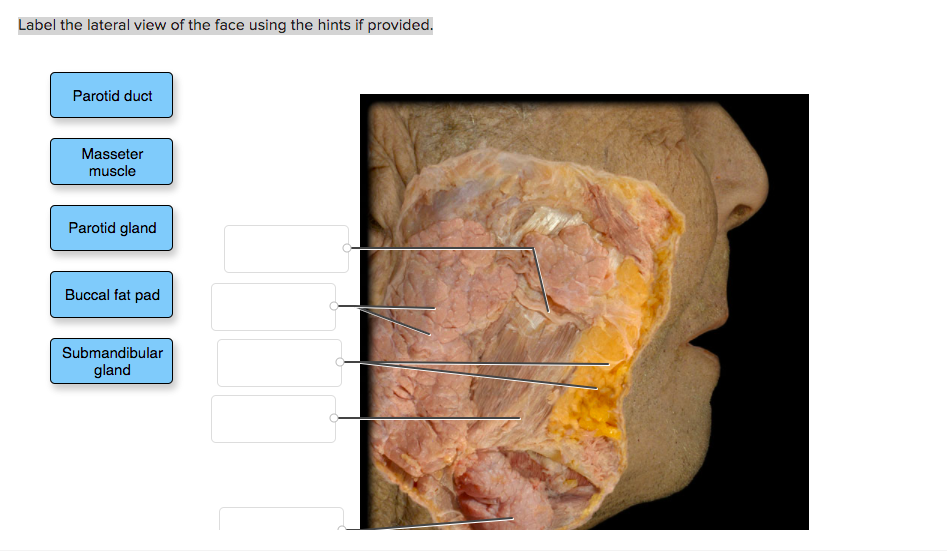
Solved Label the lateral view of the face using the hints
4. Leg 4: lateral wall of the maxillary antrum. 5. Look for fractures and look for: a fluid level (blood from a fracture) in the maxillary antrum; sinus air in the soft tissues or in the orbit. Always apply this rule : If any one of the legs is fractured then always, always, double check whether the other three legs of the midface stool are.

Muscles of the face (lateral view) Diagram Quizlet
The facial vein is a large vessel of the face and is much less tortuous than the artery of the same name. It lies posterior to the facial artery and begins from the lateral side of the nose. It drains the external palatine vein and will go on to join the retromandibular vein. This then forms the common facial vein.

Male head, lateral view Stock Image C020/0210 Science Photo Library
The lateral borders of the upper face terminate around the temporal region. The upper face region contains the forehead, eyes, and temporal region. Forehead The forehead is the superior region of the upper face region. The superficial layer of the forehead is made up of skin. Deeper to the skin layer of the forehead is the fat pads.

Face Male Left Lateral Image
lateral to include the skin margin orientation portrait detector size 24 cm x 30 cm 2 exposure 75-80 kVp 20-25 mAs SID 100 cm 2 grid yes (this can vary departmentally) Image technical evaluation the petrous ridge should be inferior to the maxillary sinuses assess for rotation via the assessments of the coronoid process symmetry

Dentistry lectures for MFDS/MJDF/NBDE/ORE Radiographic Anatomy of
1/7 Synonyms: none The human skull consists of about 22 to 30 single bones which are mostly connected together by ossified joints, so called sutures. The skull is divided into the braincase ( cerebral cranium) and the face ( visceral cranium ). The main task of the skull is the protection of the most important organ in the human body: the brain.

Muscles of the face and neck lateral view (2) Diagram Quizlet
The crease or fold of skin running from the lateral margin of the nose, where nasal base meets the skin of the face, to a point just lateral to the corner of the mouth is less prominent than usual. Synonym: Nasolabial crease, underdeveloped. Replaces: Nasolabial crease, hypoplastic; Nasolabial fold, hypoplastic.